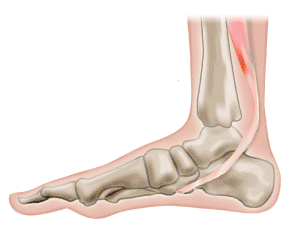
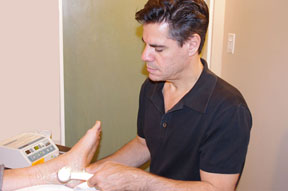
 Posterior tibial tendonitis is an injury to the tendon that connects the posterior tibialis muscle to the foot. This tendon helps turn the foot during walking, and it also supports the arch of the foot. Trauma or repetitive stress can injure the posterior tibial tendon, producing pain and swelling on the inner side of the foot or ankle. Patients may experience gait problems, and some may develop a flat foot, or their toes may point inwards or outwards. Treatment in the early stages includes resting the tendon, either by modifying activities or using a shoe insert or a cast. Anti-inflammatory medication is usually recommended. Physical therapy may include ultrasound and massage to reduce pain and swelling, and exercises to strengthen and improve range of motion in the muscles that support the foot’s arch.
Posterior tibial tendonitis is an injury to the tendon that connects the posterior tibialis muscle to the foot. This tendon helps turn the foot during walking, and it also supports the arch of the foot. Trauma or repetitive stress can injure the posterior tibial tendon, producing pain and swelling on the inner side of the foot or ankle. Patients may experience gait problems, and some may develop a flat foot, or their toes may point inwards or outwards. Treatment in the early stages includes resting the tendon, either by modifying activities or using a shoe insert or a cast. Anti-inflammatory medication is usually recommended. Physical therapy may include ultrasound and massage to reduce pain and swelling, and exercises to strengthen and improve range of motion in the muscles that support the foot’s arch.